
How to Align IP Strategy with Commercial Goals: A 10-Step Patent-to-Product Framework
Table of Contents
ToggleCompanies don’t lack ideas. They lack a structured path after patents are filed.
A strong IP commercialization strategy starts with business outcomes, maps IP to customer problems, and selects the right go-to-market path. It emphasizes cross-functional ownership, industry context, and disciplined execution.
When done correctly, this becomes a scalable IP strategy for product commercialization, enabling turning patents into products, revenue streams, and long-term competitive advantage.
Continue reading to learn more.
Introduction: Where IP Momentum Gets Lost
Most companies don’t struggle with ideas.
They struggle with what to do after the patent is filed.
Somewhere between invention disclosures and real customers, momentum dies — not because the IP lacks value, but because IP strategy with commercial goals was never clearly aligned with product direction.
This disconnect between IP strategy vs product strategy is where commercial opportunity disappears.
If you’ve ever asked:
- How do we actually start monetizing intellectual property?
- Why isn’t our IP contributing to revenue?
- Are we building products around IP — or in isolation from it?
This guide outlines a practical patent to product strategy grounded in execution — not theory — designed to support IP strategy for business growth across startups and enterprises.
Why IP Strategy and Product Strategy Drift Apart
Many organizations unintentionally separate:
- Legal protection
- R&D innovation
- Commercial revenue
But true value emerges only when IP commercialization strategy becomes embedded into product planning.
That is the foundation of enterprise IP strategy alignment.
Without this alignment, even strong IP assets fail to support scalable IP-driven product development.
10 Steps to Align IP Strategy with Commercial Goals
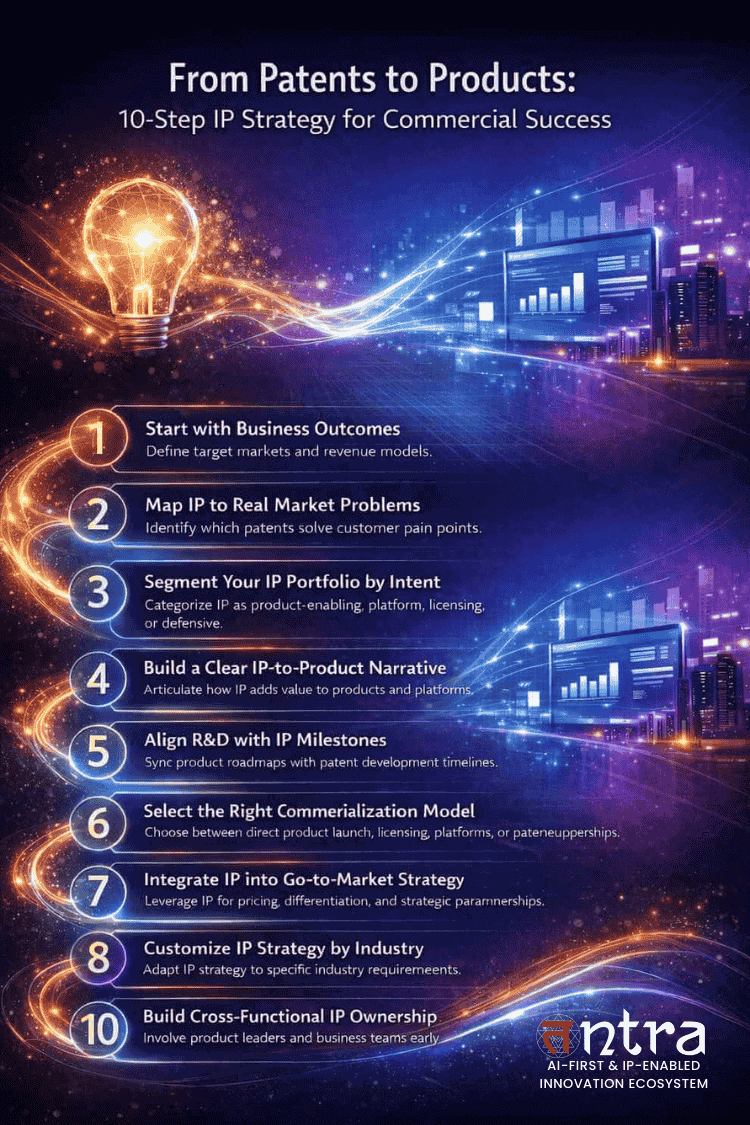
Step 1: Start With Business Outcomes, Not Patents
Before reviewing filings, define:
- Target markets
- Core customer pain points
- Revenue models (product, licensing, ecosystem, partnership)
This shift strengthens IP strategy for product commercialization and ensures IP supports growth priorities.
It is the first step toward disciplined strategic IP planning for enterprises.
Step 2: Map IP Assets to Real Market Problems
Each patent should answer:
What real-world problem does this solve better than alternatives?
This reveals:
- Which assets enable IP-led product innovation
- Which support licensing models
- Which lack commercial viability
This evaluation creates clarity in your IP portfolio commercialization approach and moves beyond defensive filing.
Step 3: Segment Your IP Portfolio by Commercial Intent
A structured commercial IP strategy framework categorizes IP into:
- Product-enabling IP
- Platform/ecosystem IP
- Licensing/royalty IP
- Defensive IP
This segmentation enables smarter execution within a broader IP to product commercialization model.
Step 4: Build a Clear IP-to-Product Narrative
Products don’t sell because they’re patented.
They sell because they solve problems uniquely.
Your teams must clearly articulate:
- How IP creates user value
- Why replication is difficult
- How it supports sustainable differentiation
This is central to scaling IP-led product innovation, particularly when collaborating with product engineering services or pursuing funding.
Step 5: Align R&D Roadmaps With IP Milestones
Execution gaps often emerge when patent timelines and product roadmaps drift apart.
A structured IP-led innovation framework ensures:
- Patent claims support future features
- IP strengthens defensibility at launch
- Innovation supports revenue timing
This discipline strengthens IP strategy for startups and enterprises alike.
Step 6: Select the Right Patent Commercialization Framework
There is no universal commercialization path.
The right patent commercialization framework depends on:
- Market maturity
- Competitive pressure
- Capital availability
- Risk tolerance
Common paths include:
- Direct product launches
- Licensing models
- White-label partnerships
- Platform ecosystems
- Joint ventures
Selecting the right IP to product commercialization model is critical to effective monetizing intellectual property.
Step 7: Integrate IP Into Go-to-Market Strategy
IP must influence pricing, positioning, and partnerships.
Strong organizations use IP to:
- Support premium pricing
- Build enterprise trust
- Strengthen sales narratives
- Enable strategic alliances
This is especially relevant in:
- Enterprise software IP strategy
- SaaS IP monetization strategy
- Competitive B2B environments
IP directly impacts defensibility within broader digital transformation strategy initiatives.
Step 8: Customize IP Strategy by Industry Context
IP behaves differently across industries.
- IP strategy in fintech innovation must balance speed and regulatory oversight
- Healthcare IP commercialization requires compliance-driven execution
- IP-led digital transformation focuses on data platforms and scalable ecosystems
Contextual execution improves long-term enterprise product modernization efforts.
Step 9: Build Cross-Functional Ownership
IP success cannot sit solely within legal teams.
High-performing organizations:
- Involve product leadership
- Educate commercial teams
- Engage an intellectual property specialist
- Integrate IP into broader intellectual property consulting services strategy
This approach strengthens both IP innovation initiatives and sustainable IP strategy for business growth.
Step 10: Treat IP as a Living Commercial Asset
IP must evolve with market direction.
That requires:
- Regular portfolio audits
- Alignment with product pivots
- Retirement of non-performing IP
This mindset transforms static filings into dynamic assets within a broader enterprise software IP strategy and long-term growth model.
Bringing It All Together: From Protection to Competitive Advantage
When executed properly, IP is not a legal checkbox.
It becomes a growth lever embedded within:
- Product planning
- Revenue strategy
- Market positioning
- Competitive differentiation
Aligning IP strategy with commercial goals requires structured thinking, collaboration, and disciplined execution.
Whether scaling IP strategy in fintech innovation, advancing healthcare IP commercialization, or driving platform-based IP-led digital transformation, the principle remains:
Start with business value.
Design for differentiation.
Execute through commercialization.
Start Your Patent-to-Product Journey
At Tntra, our IP practice, IP-led innovation services, and intellectual property services help enterprises align patents with real commercial outcomes.
Through structured R&D and innovation consulting, advanced product engineering services, and enterprise-focused intellectual property consulting services, we help organizations build scalable IP strategy models that drive measurable growth.
Connect with our experts to transform your patents into revenue-generating products.
FAQs
What is IP commercialization strategy?
An IP commercialization strategy is a structured plan for converting patents and intellectual property into revenue-generating products, licensing agreements, partnerships, or platforms. It connects legal assets with measurable commercial outcomes.
How do companies turn patents into products?
Companies apply a structured patent to product strategy by:
- Mapping patents to real market problems
- Aligning R&D with revenue goals
- Selecting the right IP to product commercialization model
- Embedding IP into go-to-market execution
Why is IP strategy important for product success?
A strong IP strategy for product commercialization improves differentiation, defensibility, pricing power, and long-term scalability — directly influencing competitive advantage.
How do you align IP with business strategy?
Through disciplined enterprise IP strategy alignment, companies begin with business objectives and design IP portfolios to support revenue models, markets, and growth priorities.
What are the best ways to monetize intellectual property?
Effective methods of monetizing intellectual property include:
- Direct product commercialization
- Licensing agreements
- Platform monetization
- Joint ventures
- Strategic ecosystem partnerships
How does IP impact go-to-market strategy?
IP strengthens positioning, pricing, and partnership leverage — particularly in SaaS IP monetization strategy and competitive enterprise software IP strategy environments.





